Get Involved/development/Tutorials/Using Qt Designer
Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar
Qt Designer User Interfaces in KDE
In this tutorial, we will explore how to programatically insert user interfaces (UIs) created with Qt Designer, into your KDE project.
Designing the UI
Qt Designer is a graphical program which allows you to easily build user interfaces, using a drag n drop interface. Here is a short example how it can go, for more information read the user documentation.
- Step 0
Call Qt Designer
designer
- Note
You can also use Qt Designer from within the QtCreator IDE (here is how).
- Step 1
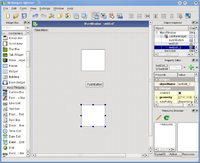
Add the widgets you want by drag-and-drop
- Step 2
Select the mainwindow
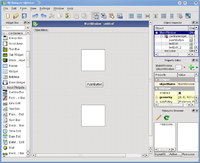
- Step 3
Select grid layout
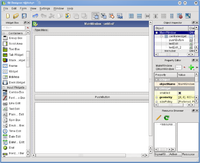
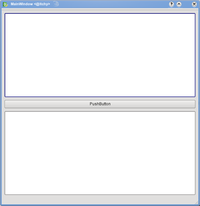
- Result
You get a decent look, and if you resize the window, the widgets resize as well.
Adding the UI File to Your KDE Project
For our purposes, the most important part of using Designer is the *.ui file that it creates. This is simply an XML file that encodes the user interface in a machine-readable (and human-readable!) way.
Let's imagine that you've created a UI named "MyDialog" with Designer, and saved it as the file mydialog.ui. To add this UI to your KDE project, simply add a command like the following to your CMakeLists.txt file:
kde4_add_ui_files(myapp_SRCS mydialog.ui)
Replace "myapp_SRCS" with the name of the main block in your CMakeLists.txt file, defining all of the source code files. It is usually the name of your application, with "_SRCS" appended.
When you do this, the build system will run the Qt program uic on mydialog.ui, to auto-generate a C++ header file that defines the UI. The generated file will be named ui_mydialog.h.
Using the UI in Your Code
The ui_mydialog.h file defines a class named "Ui_MyDialog", that contains all of the widgets you created in Designer as public members of the class. It also contains the public function "setupUi(QWidget *parent)", which instantiates all of the widgets, sets up their properties, and inserts them into layout managers, all according to what you specified in Designer.
Note that setupUi() takes a QWidget* argument. This argument represents the parent container widget, into which all of the widgets in your UI will be inserted. In other words, Ui_MyDialog is not itself derived from QWidget, and it does not contain a toplevel widget itself. You have to supply the toplevel widget when you call setupUi(). This is an important point.
One more important semantic detail: the Ui_MyDialog class also creates a Ui namespace, which simply creates an alias for the class. So you can use Ui::MyDialog to refer to the same class.
Now, on to actually using the generated UI in your code. The Qt documentation shows three ways of how to use ui-files; here only the direct approach is discussed. The goal is to create a KDialog which embeds the UI from the ui-file. First, we have to subclass MyDialog from KDialog and add a member variable of type Ui::MyDialog. The header file of "mydialog.h" looks like the following:
- ifndef MYDIALOG_H
- define MYDIALOG_H
- include <KDialog>
// include the automatically generated header file for the ui-file
- include "ui_mydialog.h"
class MyDialog : public KDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyDialog( QWidget *parent=0 );
~MyDialog();
private slots:
void slotButtonClicked();
private:
// accessor to the ui. we can access all gui elements
// specified in Designer. If mydialog.ui contains a
// button "myButton", we will be able to access it
// with ui.myButton in the cpp file.
Ui::MyDialog ui;
};
- endif
Now we are going to look at the implementation of MyDialog, which is in the file "mydialog.cpp".
- include <KLocale>
- include <KMessageBox>
// include the header file of the dialog
- include "mydialog.h"
MyDialog::MyDialog( QWidget *parent )
- KDialog( parent )
{
QWidget *widget = new QWidget( this );
// create the user interface, the parent widget is "widget"
ui.setupUi(widget); // this is the important part
// set the widget with all its gui elements as the dialog's
// main widget
setMainWidget( widget );
// other KDialog options
setCaption( i18n("This is my Dialog window!") );
setButtons( KDialog::Close );
// Example Signal/Slot connection using widgets in your UI.
// Note that you have to prepend "ui." when referring
// to your UI elements.
connect( ui.myButton, SIGNAL( clicked() ),
this, SLOT( slotButtonClicked() ) );
}
MyDialog::~MyDialog()
{
}
void MyDialog::slotButtonClicked()
{
KMessageBox::information( this,
i18n("You pressed the button!" ),
i18n( "Hooray!" ) );
}
- include "mydialog.moc"
So, basically, we create a new Ui::MyDialog and then call ui.setupUi(widget) in the constructor of MyDialog. This places the UI elements into the given widget. Then we set the parent-widget as the KDialog's main widget. We can then interact with all of the UI elements by prepending "ui." to their names, just like it is often done with the prefix "m_".
Final Thoughts
The cascade of files and classes in this tutorial may seem daunting at first, but the naming scheme layed out here has one nice intuitive feature: the source code files that you will be editing directly (either as text or with Designer) are all named with the same scheme:
- mydialog.ui: the user interface, created with Designer
- ui_mydialog.h: auto-generated by uic, Qt's user interface compiler
- mydialog.h/cpp: the dialog implementation
The steps in short are
- create mydialog.ui
- create mydialog.h/cpp
- add variable Ui::MyDialog ui; in mydialog.h
- call ui.setupUi(widget);
- access the ui elements with ui.
Qt Documentation
The Qt documentation contains a good article about Using a Component in Your Application.