Get Involved/development: Difference between revisions
kcalc is a simpler application than dolphin |
For supported operating systems (OSes), it installs all of the OS packages needed in order to build all of the KDE Frameworks 5 |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
Next, we need a method of '''managing dependencies'''. Every software has dependencies: other pieces of software that provide the functionality they rely on. In order to compile any piece of software, its dependencies must be available. | Next, we need a method of '''managing dependencies'''. Every software has dependencies: other pieces of software that provide the functionality they rely on. In order to compile any piece of software, its dependencies must be available. | ||
Most Linux-based operating systems do not provide development packages that are up-to-date enough for working on KDE software, so we will compile all the KDE dependencies ourselves. To do this, we use a command-line tool called <code>kdesrc-build</code> to download, manage, and build KDE source code repositories. Let's set it up now! First, we create a new directory for all the KDE source code we will be using; you will need many GB of free disk space. Budget 50 | Most Linux-based operating systems do not provide development packages that are up-to-date enough for working on KDE software, so we will compile all the KDE dependencies ourselves. To do this, we use a command-line tool called <code>kdesrc-build</code> to download, manage, and build KDE source code repositories. Let's set it up now! First, we create a new directory for all the KDE source code we will be using; you will need many GB of free disk space. Budget 50 GB for Frameworks + Plasma, and 10-30 more for some apps as well. We then clone the source code repository that holds <code>kdesrc-build</code> in that directory, so we have a local copy of it on our computer. | ||
{{Input|1=<nowiki> | {{Input|1=<nowiki> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
{{Input|1=<nowiki> | {{Input|1=<nowiki> | ||
# For supported operating systems (OSes), it installs all of the OS packages needed in order to build all of the KDE Frameworks 5. | |||
./kdesrc-build --initial-setup | ./kdesrc-build --initial-setup | ||
source ~/.bashrc | source ~/.bashrc | ||
Revision as of 03:59, 2 January 2023

By joining the ranks of KDE developers, you will get to implement new features and defeat bugs both daunting and simple, all while collaborating to make coherent and stable releases. Developers collaborate in teams based on what area they are working in. These can be small teams working on a single application, up to large teams working on a group of related pieces of software. Many developers are in more than one team.
KDE runs or participates in several mentoring programs to help new developers, including an informal list of people who are willing to help newcomers get started. See the Mentoring page for more details.
New to C++/Qt software development?
Most KDE software is written in C++ using the Qt toolkit and KDE Frameworks. Though prior experience with these technologies or other programming languages is helpful, you don't need to be a C++ programmer to get started! For example, no programming knowledge whatsoever is required to do things like improve text labels.
If you'd like to dive deeper, the Qt wiki contains a list of online books for learning Qt programming. Qt also provides lots of examples you can look at. For visual learners, this YouTube playlist of QML tutorials by KDE patron KDAB may be useful. Finally, information about KDE Frameworks can be found on the KDE Developer Platform and KDE API website.
One-time setup: your development environment
Source code for KDE software lives at https://invent.kde.org. But before you can work on it, you'll need to set up a development environment: a set of tools that allows you to access and edit the source code, compile it into a form that the computer can run, and deploy it to a safe location. We will now go through the process of setting one up. To accomplish these tasks, you will need to enter commands using a terminal program, such as KDE's Konsole (but any terminal program will suffice).
If you're not familiar with the command line interface, you can find a reasonable tutorial here. However, advanced command-line skills are not required, and you will learn what you need along the way!
Video version
If you are a visual learner, you might consider watching the video version at https://www.youtube.com/embed/B4xoc0K5iA4
Install basic tools
Set up kdesrc-build - Step 1/6.
First you will need to use your operating system's package manager to install some basic tools:
- Arch/Manjaro:
sudo pacman -S git cmake dialog extra-cmake-modules - Fedora:
sudo dnf install git cmake dialog perl perl-IPC-Cmd perl-MD5 perl-FindBin - KDE Neon/Kubuntu/Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt install git cmake dialog - openSUSE Leap & Tumbleweed:
sudo zypper install git breezy cmake dialog
Configure Git
We need to set your authorship information properly so that any changes you make can be properly attributed to you:
git config --global user.name "Your Name" git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
In order to authenticate yourself when pushing code changes, you need to add an ssh key to your GitLab profile as described here.
Set up kdesrc-build
Set up kdesrc-build - Step 2/6.
Next, we need a method of managing dependencies. Every software has dependencies: other pieces of software that provide the functionality they rely on. In order to compile any piece of software, its dependencies must be available.
Most Linux-based operating systems do not provide development packages that are up-to-date enough for working on KDE software, so we will compile all the KDE dependencies ourselves. To do this, we use a command-line tool called kdesrc-build to download, manage, and build KDE source code repositories. Let's set it up now! First, we create a new directory for all the KDE source code we will be using; you will need many GB of free disk space. Budget 50 GB for Frameworks + Plasma, and 10-30 more for some apps as well. We then clone the source code repository that holds kdesrc-build in that directory, so we have a local copy of it on our computer.
# If you have an old installation of kdesrc-build and you want a clean kdesrc-build installation, run a command line like: # mv ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc~bak ; mv ~/kde ~/kde~bak mkdir -p ~/kde/src cd ~/kde/src/ git clone https://invent.kde.org/sdk/kdesrc-build.git && cd kdesrc-build
Next, it's time to set up kdesrc-build and pick up the changes it made to your ~/.bashrc (or ~/.zshrc for zsh users) for the current terminal session:
# For supported operating systems (OSes), it installs all of the OS packages needed in order to build all of the KDE Frameworks 5. ./kdesrc-build --initial-setup source ~/.bashrc # Check that the command line above has worked by seeing if the PATH environment variable contains "~/kde/src/kdesrc-build". echo $PATH
The initial setup tries to install the packages, from your Linux/BSD distribution, that are needed for compiling Qt and KDE software. It also creates a ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc configuration file.
If you want a more guided setup process for kdesrc-build, run the command kdesrc-build-setup instead. However, unlike --initial-setup, it won't install packages from your distro for compiling programs so you will have to do that yourself.
Consult the kdesrc-build manual and Readme #1, Readme #2, Document #3 for more information and options.
Set up Qt
Qt is the fundamental framework that is needed for pretty much all KDE development. We need a recent enough version of Qt to proceed. If you are just getting started, we recommend that you use a Linux distribution that is better suited for kdesrc-build either as the primary operating system or in a virtual machine.
You can look up the version of the Qt framework installed on your operating system by opening the application "Info Center" (KInfoCenter) > Basic Information > About this System > "Qt Version:". Or starting any installed KDE application (e.g. the KDE calculator app (kcalc)) and from the application's main menu > Help > About application > Components tab > "Qt".
If you have Qt 5.15 or any later version installed, you are already done with the "Set up Qt" step and can proceed to the next section. 🎉
...otherwise we now need to install a more recent version from somewhere. Your distribution might have one available. Alternatively, we need to configure kdesrc-build to build and install a recent Qt version for you. Building Qt using kdesrc-build is a more advanced topic.
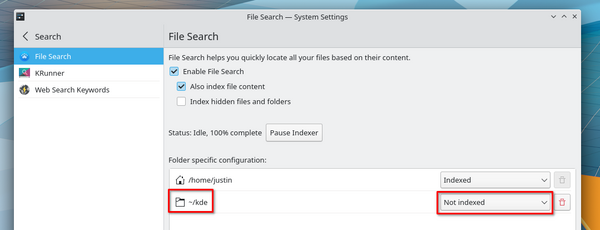
Disable indexing for your development environment (optional)
You'll want to disable indexing for your development-related git repos and the files they will build and install. Add ~/kde to the exclusions list in System Settings > File Search, like so:
Download non-KDE dependencies
Set up kdesrc-build - Step 3/6.
If your distribution is supported, kdesrc-build --initial-setup will install the distribution packages which are needed in order to build KDE software. kdesrc-build is used in order to build any of the KDE git repositories. The packages for Qt and the rest of the dependencies are acquired using your Linux distribution's package manager.
Reboot your computer and log back in so the package changes, and the changed ~/.bashrc take effect on your user account.
Once that's done, your development environment is set up and ready to build software! Let's take it for a spin.
Building software with kdesrc-build
It can take an hour or more to compile a KDE application, Framework, or Plasma itself for the first time. The reason for this is that kdesrc-build is compiling all of the KDE Frameworks 5 modules plus any other KDE module that is a dependency of the module that you tell kdesrc-build to build.
kdesrc-build by default has the option "--include-dependencies" enabled so it will ignore all KDE packages that were installed using the distribution's package manager and will instead build all needed KDE modules from source.
The next time you want to compile that or any other piece of KDE software, it will be much faster since most of the dependencies will have already been compiled. If you don't want to build all dependencies (e.g., because you are using a rolling release distro that provides recent versions of software), edit the same configuration file and simply set include-dependencies to false or add the --no-include-dependencies option when running kdesrc-build.
KDE Frameworks
Set up kdesrc-build - Step 6/6.
KDE Frameworks are libraries of tools and features that can be used by any application or Plasma itself. New versions of KDE Frameworks are released once a month. A list of all of the frameworks can be found here: https://api.kde.org/frameworks.
After you install all of the dependencies needed in order to build all of the KDE Frameworks, the first thing that you should do using kdesrc-build is to build all of the KDE Frameworks:
kdesrc-build frameworks
Applications
KDE Applications like Calculator (KCalc), Dolphin, Okular, Konsole and Gwenview are standalone apps that can be run on multiple platforms, such as Plasma, GNOME, even macOS and Windows! New versions of KDE Applications are released three times a year. Note that the Discover app store (git repo name: plasma-discover) and System Settings app (git repo name: systemsettings) are distributed alongside Plasma, but they build like apps using the below instructions. A list of all KDE applications can be found here: https://apps.kde.org/.
The general steps required to build and run an application are described in the following using kcalc as an example:
kdesrc-build kcalc
As a part of this process, kcalc was installed to ~/kde/usr/bin/kcalc. There is no need to manually install anything; kdesrc-build installed it for you! Source the project's auto-generated prefix.sh file every time you want to run your custom-compiled version of kcalc:
source ~/kde/build/kcalc/prefix.sh kcalc # You can check that "/home/username/kde/usr/bin" is the first directory in $PATH. # echo $PATH
Or using the kdesrc-run command:
kdesrc-run kcalc
Did it run? If so, then congratulations, you just compiled your own version of the KDE calculator (kcalc) from source code!
Plasma
KDE Plasma is the environment in which you can run apps. Plasma is responsible for providing a desktop with wallpaper, app launchers, and widgets; displaying notifications; managing wired and wireless networks; and similar operating-system level tasks. New versions of Plasma are released three times a year. Plasma has multiple shells: Plasma Desktop for desktop, laptop, and 2-in-1 computers, Plasma Mobile for mobile phones, Plasma Bigscreen for televisions, and so on. They all share certain common components, such as a window manager, networking stack, basic graphical components, and so on. Here is how to build them:
kdesrc-build plasma-workspace plasma-framework plasma-integration bluedevil powerdevil plasma-nm plasma-pa plasma-thunderbolt plasma-vault plasma-firewall plasma-workspace-wallpapers kdeplasma-addons krunner milou kwin kscreen sddm-kcm plymouth-kcm breeze discover print-manager plasma-sdk kaccounts-integration kaccounts-providers kdeconnect-kde plasma-browser-integration xdg-desktop-portal-kde kde-gtk-config khotkeys kgamma5 breeze-gtk drkonqi phonon flatpak-kcm --include-dependencies
Plasma Desktop
To build the Plasma Desktop environment and its related apps, also build the following:
kdesrc-build plasma-desktop systemsettings plasma-disks plasma-systemmonitor ksystemstats kinfocenter kmenuedit --include-dependencies
To get translations in your self-built Plasma, you must build plasma-workspace with -DKDE_L10N_SYNC_TRANSLATIONS=true. The easiest way to do this is go into the build directory (~/kde/build/plasma-workspace by default), run ccmake ., turn on that setting, and then rebuild the project.
Now it's time to make your built-from-source Plasma session accessible from the SDDM login screen, and also copy the built-from-source DBus files into a location where they are visible to them system bus. To do this, run the following command:
~/kde/build/plasma-workspace/login-sessions/install-sessions.sh
After this, you can log out and select your new plasma session in SDDM's session chooser menu (which is located in the bottom-left corner of the screen if you're using the Breeze SDDM theme).
Alternatively, you can run the new version of plasma on top of your existing system for quick testing like so:
source ~/kde/build/plasma-desktop/prefix.sh ~/kde/usr/bin/plasmashell --replace
Plasma Mobile
To build the Plasma Mobile environment, also build the following:
kdesrc-build plasma-nano plasma-mobile plasma-settings --include-dependencies
You can run your custom-built Plasma Mobile in a phone-sized window within your existing session like so:
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/tmp/ export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=wayland export QT_QPA_PLATFORMTHEME=KDE export QT_WAYLAND_DISABLE_WINDOWDECORATION=1 export XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP=KDE export KSCREEN_BACKEND=QScreen export KDE_FULL_SESSION=1 export KDE_SESSION_VERSION=5 export QT_QUICK_CONTROLS_MOBILE=1 export PLASMA_PLATFORM=phone:handheld export $(dbus-launch) dbus-run-session kwin_wayland --width 360 --height 720 --xwayland "plasmashell -p org.kde.plasma.phoneshell"
Plasma Mobile can also be run on a mobile device itself. For information on how to do that, see https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Mobile/DevGuide#Mobile_device_running_plasma_mobile.
For more information, see https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Mobile/DevGuide.
Iterating on a single project
When you're working on a project and you want to rebuild it to test your changes, you can save a lot of time by only rebuilding that project, rather than the entire stack. For example if you are working on plasma-desktop, you can rebuild only that project rather than everything by running kdesrc-build --no-src --no-include-dependencies plasma-desktop.
How to solve build problems
Did one or more modules fail to build (displayed in red font) using kdesrc-build? Here's what to do:
- Try building the failing module again from scratch using
kdesrc-build [failing module] --refresh-build - Make sure that you have all the dependencies for the failing module. Go back to the #Download non-KDE dependencies section and re-install the non-KDE dependencies. If that doesn't fix the problem, open the log file for the failing module, which
kdesrc-buildwill print the path at the end of its output. Scroll to the bottom of the log file and read the output to see what missing dependency it is complaining about. Then find and install the corresponding package using the package manager of your distribution. If several look relevant, install them all just to be safe. When you have the necessary dependencies, you can save time and resume from the failing module by adding--resume-from [the name of the module that failed]to yourkdesrc-buildcommand. - Check the list of currently broken modules on the KDE build server. If it's broken there, then it's not your fault. :)
- Ask for help in the the #kde-devel channel on Matrix or Libera Chat IRC. See Get Involved/development#Communicate with the team
- Looking into the error log is also helpful. For example, the build stopped at kwallet. You will need to go into
kde/src/log/latest/kwallet/error.logand find what packages are missing. - If you know what files are missing, but you don't know what packages provide them, you can ask your package manager. See https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Pacman/Rosetta (see "Query the package which provides FILE").
- The problem might be in
~/kde/usr. E.g. a file in~/kde/usr/includewhich was renamed or moved. You can help yourself by seeing if you can reproduce this issue in a clean new Virtual Machine (VM). If you cannot reproduce the issue in your VM, then a possible solution is to start with a new and clean kdesrc-build installation. I.e. run something likemv ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc ~/.config/kdesrc-buildrc~bak ; mv ~/kde ~/kde~bak. Then install kdesrc-build from scratch using this wiki page.
Choose what to do
Now that you can compile and deploy custom versions of KDE software, you can open your editor and start hacking on the source code! The code for the version of Dolphin that you built earlier is located at ~/kde/src/dolphin/; other projects you build with kdesrc-build will live in similar locations.
You may wish to look over the instructions for setting up an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for development with KDE projects.
A good place to start is with a small bug or feature in an existing piece of software that affects you personally ("scratch your own itch"). Get in touch with the existing developers (see Communicate with the team, below) and they can help you out, by pointing you to the right place in the code and giving advice about how to tackle the problem.
Try not to start by proposing or working on major features or significant design changes. These can be controversial, and the smoothest way to get going is by working on relatively non-controversial bugfixes. Start slowly and build trust!
Here are some other ideas for starting points:
- Improve awkwardly-worded messages and labels that are written in English. This is a great way for non-programmers to contribute! If you can compile software and have a good grasp of English, you can make a big difference here.
- Work on Junior Jobs, which are small tasks that are suitable for beginners (both bugs and features).
- Work on Bugs related to KDE's Usability & Productivity initiative, many of which are small and easy.
- More easy tasks.
Test your changes
Once you've made some changes, make sure the project still compiles and installs, and make sure the changes have the desired effect when you run the software. Then it's time to run the project's unit tests:
cd ~/kde/build/dolphin/ source ./prefix.sh ctest --output-on-failure
If any test fails, that needs to be investigated and fixed before you can proceed. Once the tests pass, then run the software again to make sure it still behaves properly. If it doesn't, then go back and work on your patch some more, then re-compile and re-deploy, and test again, until the program does what you'd like it to do and all tests pass.
Submit a Merge Request
Once you're happy with your patch and have verified that it does what you want, it's time to submit your changes for the review!
KDE uses GitLab for merge request submission and review. Learn how to submit a Merge Request with GitLab.
Communicate with the team
There are several ways to get in touch with KDE developers, either generally or for a specific project. The most important communications channels are:
- The #kde-devel channel on Matrix or the Libera Chat IRC, which is where KDE developers chat in real-time about their work.
- The kde-devel mailing list is the primary development mailing list. Learn more about mailing lists.
These are general KDE development communication channels, and you may get directed to a more appropriate place for the project you are interested in. There is a list of mailing lists if you want to find a mailing list for a specific team directly. Many teams have their own real-time chat channels, too.
You can also try looking for the team's section on the Main Page of this wiki. Many teams have information there for new contributors.
Source code cross referencing
To search for a class, method, signal name... etc in all KDE repos, KDE uses a code referencing tool to index code in the various KDE repositories, you can search using the web interface available at https://lxr.kde.org/ . This is a very useful tool if you e.g. want to search for code usage examples in existing code... etc.
Usage:
- From the Branch group menu, you can select either kf5-qt5, to search the code in the Git master branches or stable-kf5-qt5 to search only the stable (released) branches
- There are two search modes:
- On the Identifier search page, you can search for (note that this is case sensitive):
- class names, e.g. RenameDialog, StatJob, and of course any Qt class (used in KDE code, which is pretty much all of them), QLatin1String, QListWidget
- method names, e.g. addConfigSources() (from the KConfig framework) and signal names e.g. mimeTypeFound()
- on the General search page, you can search for strings, e.g. in Dolphin's context menu (accessed by right- clicking any empty space) there is Paste Clipboard Contents, if you want to find in which source file this string is defined, search for Paste Clipboard Contents; this search includes classes/methods/signals names.
- On the Identifier search page, you can search for (note that this is case sensitive):
Microsoft Windows
You can build and develop KDE projects using the Microsoft Windows operating system.
Apple macOS
You can build and develop KDE projects using the Apple macOS operating system.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) configuration
Set up graphical development tools or an Integrated Development Environment (IDE). You may want to try out KDevelop, the KDE IDE.
Next steps
Sharpen your skills by going through the KDE development tutorials.
After you have had several drama-free patches accepted, a KDE developer is likely to suggest you get a Developer account, which will allow you to commit directly to KDE projects. With very few limits on where you can commit, you will be expected to act responsibly. At this point, congratulations! You are officially a KDE developer!
Best practices & other useful information
- Lessons learned over time regarding the development of user-facing software
- Debugging
- Unit testing
- Validating code
- Writing API documentation (related: https://api.kde.org).
- Correctly state license information
- Writing Wayland-friendly code
- Porting from KDE 4 to Frameworks 5
- Running applications and their unit tests without first installing them
- How to review merge requests
- How to build with Docker
More
This page continues with more advanced topics.